In a latest research performed by the Institute of Anatomy, College of Drugs, College of Ljubljana, researchers have supplied new insights into the detrimental results of kind 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) on skeletal muscle construction and capillary networks. Using state-of-the-art 3D imaging expertise, this complete research marks a big leap in understanding the multifaceted impression of T1DM on the physique’s muscular system.
Diabetes mellitus disrupts the regulation of glucose ranges, resulting in excessive blood sugar and a myriad of associated well being points. T1DM, characterised by the immune-mediated destruction of insulin-producing pancreatic β cells, has profound results on varied organs, particularly skeletal muscle mass, which play an important position in glucose uptake and regulation.
This research, revealed within the journal Biomolecules and Biomedicine, aimed to discover the structural and purposeful variations of skeletal muscle mass to the metabolic disturbances attributable to T1DM.
The hidden modifications in muscle and blood vessels
Performed on feminine C57BL/6J-OlaHsd mice utilizing a streptozotocin (STZ)-induced mannequin to simulate T1DM, the analysis targeted on vital muscle mass just like the soleus, gluteus maximus, and gastrocnemius. Researchers meticulously analyzed the expression of myosin heavy chain (MyHC) isoforms and the intricacies of the 3D capillary community.
“Our research gives a deeper understanding of how kind 1 diabetes not solely impacts muscle fiber composition but additionally considerably alters the capillary networks which are important for muscle well being,” defined Nejc Umek, the research’s lead writer.
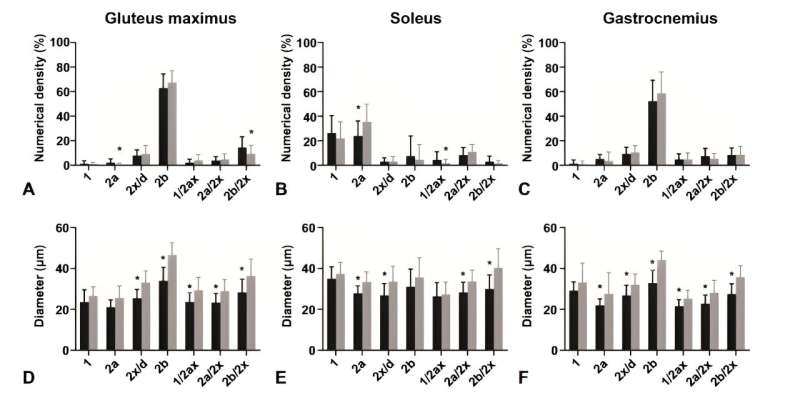
The analysis revealed that, regardless of the composition of fast-twitch kind 2b fibers remaining constant, notable variations have been noticed within the diabetic mice’s soleus muscle, which confirmed a lowered proportion of kind 2a fibers and diminished fiber diameters throughout all muscle mass analyzed.
Moreover, an intriguing improve in capillary size per muscle quantity was found within the gluteus maximus of diabetic mice, suggesting an adaptive mechanism to counterbalance muscle fiber atrophy induced by diabetes.
Methodological advances and key discoveries
The research utilized feminine mice, addressing a spot in diabetes analysis that always overlooks gender variations in illness development and response to therapy. By way of a single intraperitoneal administration of STZ, researchers efficiently induced T1DM, confirmed by considerably elevated fasting glucose ranges. This mannequin allowed for an in-depth examination of diabetes-induced modifications in a managed atmosphere.
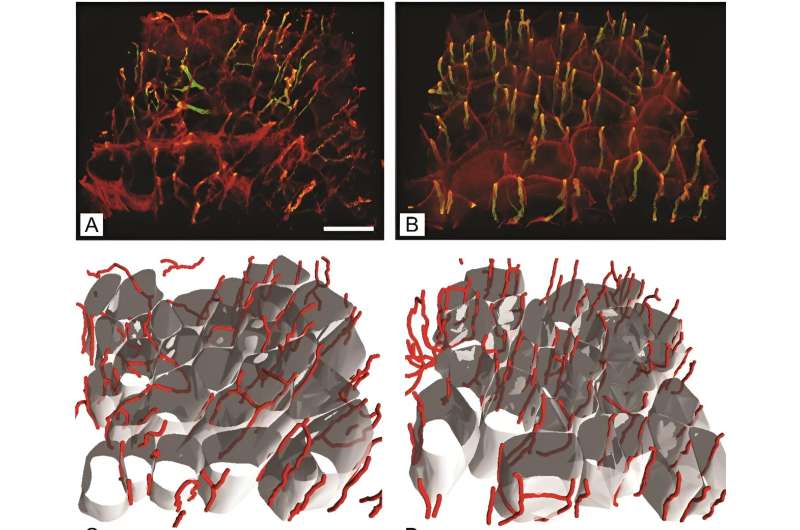
By using antibodies particular to totally different MyHC isoforms and cutting-edge 3D imaging, the crew might exactly quantify modifications in muscle fiber sorts and the capillary community. “The superior 3D imaging strategies we used signify a big enchancment over conventional 2D analyses, providing a extra detailed and correct depiction of the capillary community modifications in diabetic muscle tissue,” said Erika Cvetko, the research’s senior writer.
Implications for diabetes administration and future instructions
The findings from this collaborative analysis effort spotlight the need for complete diabetes administration plans that embody not solely glucose regulation but additionally the preservation of muscle construction and performance. “Understanding the precise alterations in muscle tissue because of kind 1 diabetes paves the best way for creating focused therapies that would considerably enhance affected person outcomes,” Cvetko added.
The research’s revelations in regards to the elevated capillary size per muscle quantity in diabetic mice underscore the physique’s potential compensatory responses to the structural modifications induced by diabetes. These insights are essential for designing interventions that goal to mitigate muscle deterioration and improve total diabetes care.
This novel research contributes considerably to the physique of data on diabetes and its systemic results, notably on skeletal muscle well being. By highlighting the vital position of sustaining muscle integrity and vascular provide within the administration of T1DM, the analysis opens new avenues for therapeutic methods and underscores the significance of multidisciplinary approaches in tackling this complicated illness.




