A synthetic pancreas that mixes an off-the-shelf glucose monitor and insulin pump with an app developed by Cambridge scientists has been efficiently trialled by folks residing with sort 2 diabetes.
The system doubled the period of time folks have been within the goal glucose vary and halved the time folks spent experiencing excessive glucose ranges.
The app, referred to as CamAPS HX, utilises an algorithm that predicts how a lot insulin is required to maintain an individual’s glucose ranges throughout the goal vary.
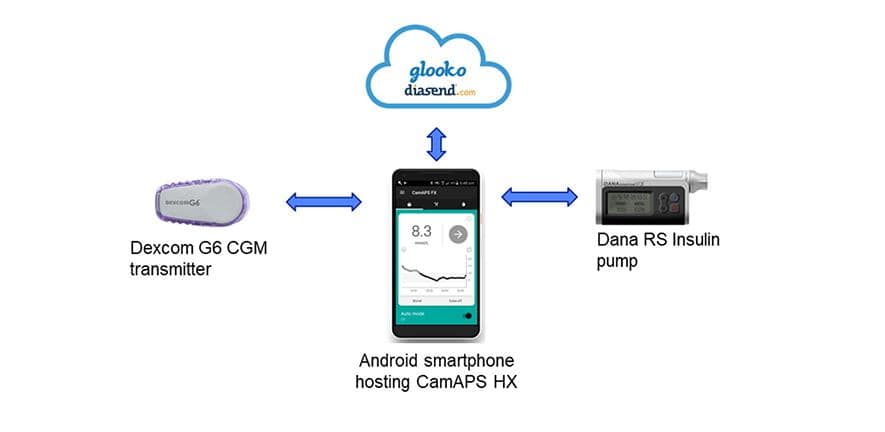
The crew has already demonstrated that a synthetic pancreas run by an analogous algorithm is efficient for folks residing with sort 1 diabetes, from adults by to very younger kids. They’ve additionally efficiently trialled the system in folks with sort 2 diabetes who require kidney dialysis.
This new model, trialled for the primary time in a wider inhabitants residing with sort 2 diabetes (not requiring kidney dialysis) is a completely closed loop system. The model for folks with sort 1 diabetes requires them to report that they’re about to eat in order that the substitute pancreas can modify insulin ranges accordingly, however the newest iteration features robotically.
Dr Charlotte Boughton from the Wellcome-MRC Institute of Metabolic Science on the College of Cambridge, who co-led the research, stated, “Many individuals with sort 2 diabetes wrestle to handle their blood sugar ranges utilizing the at present obtainable therapies, corresponding to insulin injections. The factitious pancreas can present a secure and efficient method to assist them, and the expertise is straightforward to make use of and could be applied safely at house.”
The app additionally diminished ranges of glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c). Glycated haemoglobin develops when haemoglobin joins with glucose within the blood, changing into ‘glycated’. The upper the HbA1c, the larger the danger of creating diabetes-related issues. After the management remedy, common HbA1c ranges have been 8.7%, whereas after utilizing the substitute pancreas they have been 7.3%.
Dr Aideen Daly, additionally from the Wellcome-MRC Institute of Metabolic Science, stated, “One of many boundaries to widespread use of insulin remedy has been concern over the danger of extreme ‘hypos’ — dangerously low blood sugar ranges. However we discovered that no sufferers on our trial skilled these and sufferers spent little or no time with blood sugar ranges decrease than the goal ranges.”
Suggestions from contributors prompt that contributors have been comfortable to have their glucose ranges managed robotically by the system, and 9 out of 10 (89%) reported spending much less time managing their diabetes total.
Customers highlighted the elimination of the necessity for injections or fingerprick testing and elevated confidence in managing blood glucose as key advantages. Downsides included sensible annoyances with carrying of units, and elevated nervousness concerning the threat of hypoglycaemia — which the researchers stated could mirror elevated consciousness and monitoring of glucose ranges.
The crew now plan to hold out a bigger research to construct on their findings and have submitted the system for regulatory approval with a view to creating it commercially obtainable for outpatients with sort 2 diabetes.
Examine in Nature Drugs – https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-022-02144-z
This text is republished from Hospital + Healthcare. Learn the article right here.




