Insulin is a hormone that decreases blood glucose ranges. The one cells that produce insulin are pancreatic beta cells (β-cells), and a lower in these cells is a significant explanation for diabetes. Though therapies geared toward growing pancreatic β-cells are eagerly awaited, a method that may improve β-cells has, to date, not been developed.
In a promising development, a analysis group from the Tohoku College Graduate Faculty of Drugs has revealed that stimulating autonomic vagal nerves linked to the pancreas can enhance the operate and likewise improve the variety of pancreatic β-cells in mice.
The group, which was led by Affiliate Professor Junta Imai, Assistant Professor Yohei Kawana, and Professor Hideki Katagiri, revealed their findings within the journal Nature Biomedical Engineering on November 9, 2023.
“Utilizing optogenetics, we first developed a method to stimulate individually the vagus nerve resulting in the pancreas in mice,” says Imai. “This novel methodology led to a marked elevation within the quantity of insulin within the blood when sugar was administered, indicating improved β-cell operate.”
Further stimulation of this nerve over two weeks greater than doubled the unique variety of β-cells. Stimulating the pancreatic vagal nerves activated β-cells by way of each high quality and amount.
When Imai and his colleagues utilized this methodology to a mouse mannequin of insulin-deficient diabetes, the regeneration of pancreatic β-cells ameliorated diabetes in these mice. This represents the primary profitable remedy of diabetes in mice by stimulating the vagal nerves linked to the pancreas.
“We hope our achievements result in the event of latest methods and preventive strategies for diabetes,” provides Imai. “We additionally count on it to advance our understanding of the mechanisms that regulate the operate and variety of pancreatic β-cells, in addition to the causes of diabetes.”
-
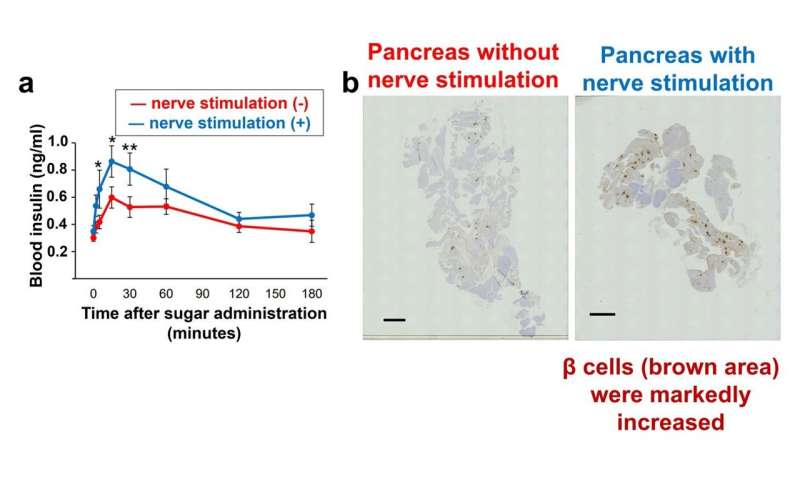
Stimulating the pancreatic vagus nerve linked to the pancreas elevated blood insulin after sugar was administered (a) and β-cell numbers (b). The brown space indicated the pancreatic β-cells clustered within the islets of Langerhans. Credit score: Junta Imai et al
-
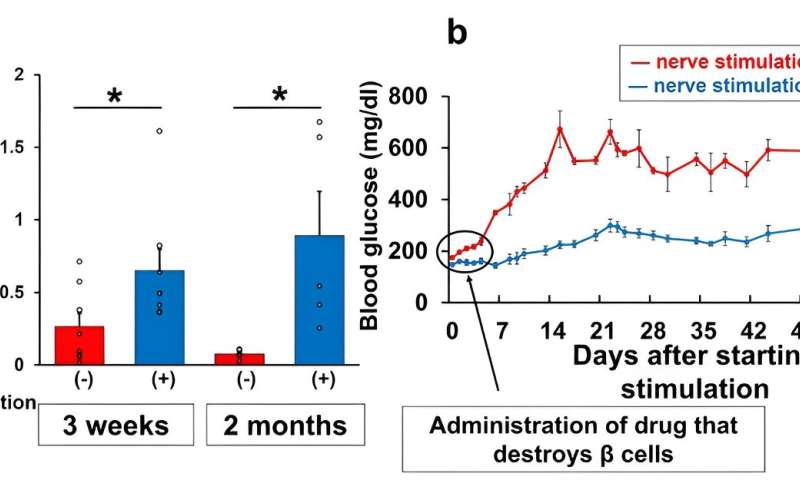
Stimulating the pancreatic vagal nerve linked to the pancreas restored depleted β-cells in diabetic mice (a) and improved blood glucose ranges. Credit score: Junta Imai et al




